Meta’s LlamaCon: The Future of Open-Source AI – 2025 Trends and Insights
Meta’s LlamaCon: A Glimpse into the Future of Open-Source AI
🌟 Have you ever thought about how AI could shape the next decade? Meta’s inaugural LlamaCon, a one-day summit for developers, gave us an inside look at how the future of open-source AI is unfolding. If you’re interested in understanding the direction of the technology and its growing impact, this event was a must-attend.
I was fortunate enough to be there and witness firsthand how Meta is playing a crucial role in the evolution of AI, especially in open-source models. From how the open-source AI community is rapidly expanding to discussions about AI agents and the future of digital content, LlamaCon brought together the brightest minds in the industry. Here’s what I learned and how it could reshape everything we know about AI.
Open-Source AI: A Thriving Ecosystem 🌐
After attending LlamaCon, one thing is clear: the open-source AI community is booming. Mark Zuckerberg himself pointed out how Meta’s Llama models have gone from 650 million downloads last December to over 1.2 billion today. That’s a huge leap in just a few months! The open-source AI landscape is evolving rapidly, with major players like Google, Mistral, and soon OpenAI contributing their own models.

Why does this matter?
Well, with so many models now available, developers are experimenting and creating derivative models, expanding the possibilities for AI. Take, for example, Nvidia’s new Llama-3.1 Nemotron Ultra, which is half the size of DeepSeek’s R1 but outperforms it. The competition is fierce, and the possibilities are endless.
But it’s not just about developers making new models—it’s also about organizations adopting these technologies. Meta’s new Llama API is a game-changer for businesses, making it easier to integrate AI into their operations. And the impact goes far beyond tech companies. Take the Crisis Text Line, for instance, which is using Llama to enhance its ability to identify people at risk of self-harm or suicide. It’s an inspiring example of how AI can save lives and be used for social good. 🌟
Voice: The Next Major Interface 🔊

Zuckerberg has long talked about the potential of voice as a key interface for AI, and he doubled down on that at LlamaCon. Think about it: voice interaction is the next natural step for AI systems. We’re already starting to see this with smart devices, but Zuckerberg envisions ultra-low latency in voice technology making it feel as seamless as talking to a human.
I completely agree. There’s something incredibly intuitive about speaking to an AI, like Tony Stark talking to Jarvis. It opens the door to new possibilities in fields like education, customer service, healthcare, and beyond. Imagine having an AI assistant that you can talk to just like a friend, helping you plan your day, get information, or even navigate complex tasks. The future is going to sound a lot more like a conversation!
The Rise of AI Agents 🤖
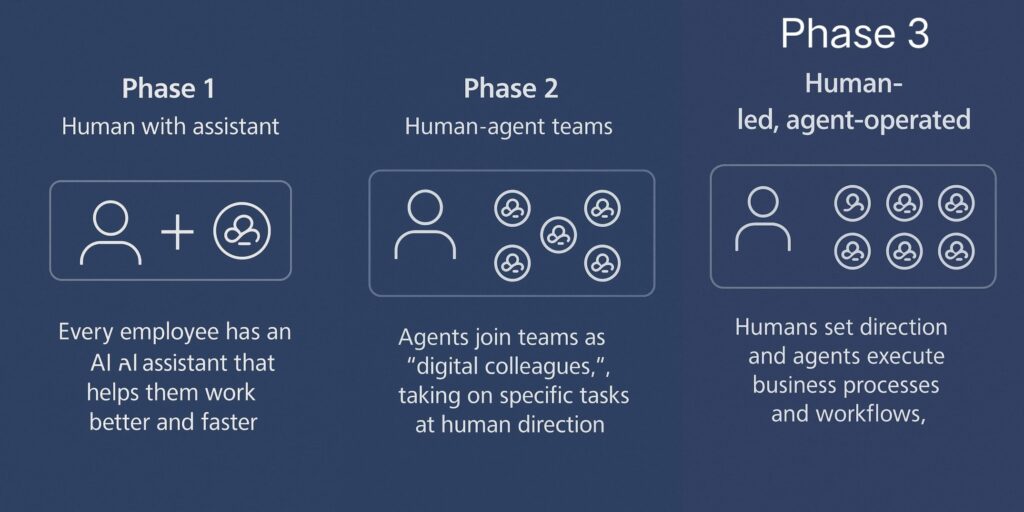
If you’ve been following AI, you’ve probably noticed the rise of “agents”—intelligent systems capable of much more than answering questions. Zuckerberg and Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella both highlighted that about 30% of their organizations’ code is already AI-generated. And they expect that number to keep growing, with entire projects being developed by AI in the near future.
What’s interesting about this shift is that AI agents are moving away from simple query-response systems like chatbots. These agents can reason, plan, take action, and reflect—all with a high degree of autonomy. This is where the real magic happens. These agents are becoming digital co-workers, capable of collaborating with humans in powerful ways.
This shift is crucial. While the policy discourse in Washington is still stuck on chatbots, in Silicon Valley, the conversation is about AI agents who can actively assist in creating things. The move from chatbots to agents isn’t just an upgrade—it’s a paradigm shift. And anyone who ignores it could miss out on the next big leap in AI innovation.
Redefining Digital Content 📝
Here’s a question to ponder: What happens when an AI system can create text, code, images, and even simulations all in one go? Satya Nadella raised this thought-provoking question during his talk. We already see AI models like ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Meta AI, and Anthropic Claude offering dynamic content generation on various levels.
Today, you can chat with a PDF, extract key insights, dive deep into research, and even generate interactive simulations—all within one AI interface. It’s mind-blowing how much AI can do, and it’s starting to redefine what we consider a “document.” Could this be the future of education, journalism, or publishing? Time will tell, but it’s clear that we’re on the edge of a new era in content creation.
Geopolitical Stakes of Open-Source AI 🌍
As exciting as these advancements are, there’s a geopolitical dimension to consider. The release of DeepSeek’s R1 in January highlighted the strategic importance of open-source AI. In the race between the US and China, open-source AI could play a crucial role in global influence. The US must ensure its open-source models dominate, not only for economic reasons but also for national security. Meta’s decision to open-source Llama is a strategic move, providing access to cutting-edge AI for countries and organizations around the world. This ensures that AI models developed in the US remain part of the global conversation, especially in regions like the Global South.
AI Agents as “Expertise-as-a-Service” 🔍
It’s no longer just about AI as a tool or software. The real shift we’re seeing is in the concept of “expertise-as-a-service.” Think about it—AI agents are becoming highly specialized assistants that can tackle complex tasks. This transformation will make high-level expertise more accessible than ever before.
Policymakers and organizations must start thinking about the implications of this shift. AI agents can empower individuals and teams in ways we never thought possible, and they will democratize access to knowledge across the globe.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Open-Source AI❓
1. What is open-source AI?
Open-source AI refers to artificial intelligence models, frameworks, or tools that are publicly available, allowing anyone to use, modify, or distribute them, usually under a permissive license.
2. Why is open-source AI important?
Because it democratizes access to advanced AI, enabling researchers, startups, educators, and even low-resourced countries to build powerful AI systems without proprietary restrictions.
3. How does open-source AI differ from closed-source AI?
Closed-source AI is developed privately and usually requires paid licenses, while open-source AI is transparent and freely available, encouraging collaboration and community innovation.
4. Who are the key players in the open-source AI space?
Major contributors include Meta (Llama), Mistral, Hugging Face, EleutherAI, DeepSeek, Google (Gemma), and even NVIDIA with models like Nemotron.
5. What are the benefits of using open-source AI models like LLaMA or Mistral?
-
Cost savings
-
Full transparency
-
Customizability
-
Community support
-
No vendor lock-in
6. Is open-source AI safe?
It can be, but it depends on how it’s used. Open-source models give you flexibility, but they also require responsible deployment and proper safeguards to avoid misuse.
7. Can I use open-source AI in commercial projects?
Yes, most open-source AI models come with licenses that allow commercial use—but always check the licensing terms (e.g., Apache 2.0, MIT, Meta’s community license).
8. What are the limitations of open-source AI?
-
Limited support
-
Security risks if misconfigured
-
May not match cutting-edge proprietary performance
-
Requires technical expertise to fine-tune
9. How do companies benefit from open-source AI?
They gain faster development cycles, reduced costs, innovation from a global community, and the ability to customize solutions for specific use cases.
10. Which open-source AI models are the most popular in 2025?
-
Llama 3 (Meta)
-
Mistral 7B and Mixtral
-
DeepSeek R1
-
Gemma (Google)
-
Nemotron (NVIDIA)
11. Is Meta’s Llama 3 really open source?
It’s open but under Meta’s “community license,” which isn’t fully permissive like MIT or Apache but still allows wide usage for research and commercial purposes.
12. What is the future of open-source AI?
It’s incredibly promising. Experts predict AI agents, voice interfaces, and collaborative tools will increasingly be built on open-source foundations for flexibility and trust.
13. What industries are using open-source AI today?
-
Healthcare
-
Education
-
Finance
-
Customer service
-
Cybersecurity
-
Manufacturing
-
Mental health (e.g., Crisis Text Line)
14. Are open-source AI tools beginner-friendly?
Some are! Tools like Hugging Face simplify access. However, deeper customization usually requires some coding and machine learning knowledge.
15. Is open-source AI more ethical than proprietary AI?
Not inherently, but the transparency of open models allows for broader ethical reviews and accountability, which is often missing in closed systems.
16. Can open-source AI beat ChatGPT or Claude?
In specific domains or with fine-tuning, yes. Some lightweight open models outperform proprietary giants in cost-efficiency or niche tasks.
17. What’s the difference between Llama 2 and Llama 3?
Llama 3 offers better reasoning, longer context windows, and more efficient training—thanks to improved data and architectural refinements.
18. How do AI agents use open-source models?
AI agents like AutoGPT or CrewAI often use open models as the reasoning backbone, allowing them to autonomously plan, execute, and reflect on tasks.
19. Where can I download open-source AI models?
-
Meta AI GitHub
-
Mistral.ai
-
DeepSeek open model hub
-
Google’s Gemma on GitHub
20. What license does Meta use for Llama 3?
It uses the Meta community license, which allows free use under guidelines (e.g., no use for surveillance, disinformation, or harm).
21. Do I need a GPU to run open-source AI?
Yes, most large models require a GPU to run efficiently. Some smaller versions (like Llama 3 8B) can run on consumer-grade hardware with optimizations.
22. Can open-source AI models be fine-tuned?
Absolutely. One of the biggest advantages is the ability to fine-tune them on custom datasets to create specialized, efficient models.
23. What is an example of open-source AI in healthcare?
Crisis Text Line uses a Llama-based model to detect signs of suicide risk with more precision than human-only monitoring.
24. Is open-source AI good for startups?
Definitely. Startups often can’t afford licensing costs for closed models, so open models allow them to scale AI capabilities affordably.
25. What is “expertise-as-a-service” in open-source AI?
It refers to AI agents powered by open models acting as digital experts, offering services like legal advice, coding help, research, etc., to anyone.
26. Are there risks of open-source AI being misused?
Yes, like deepfakes, misinformation, or spam bots. That’s why responsible licensing, transparency, and safety checks are critical.
27. Can open-source AI generate voice, code, and images too?
Yes! Many open models now support multimodal generation, handling voice synthesis, code writing, image creation, and more from a unified canvas.28. What’s a good starter model for learners?
Try Gemma 2B, TinyLlama, or Mistral 7B on Hugging Face. These are light, fast, and supported by communities.
29. How can policymakers support open-source AI?
By funding research, creating clear open-model standards, promoting digital inclusion, and collaborating with developers to align on safety frameworks.
30. Why is open-source AI important for the Global South?
Because it lowers barriers to entry, enabling countries with limited tech infrastructure to access powerful tools without depending on foreign tech monopolies.
31. How do I know if an open-source AI model is trustworthy?
Check community reviews, paper citations, reproducibility of results, and whether the model includes transparency statements and use-case limitations.
Conclusion: Embrace the Future of AI 🌟
Meta’s LlamaCon was a fascinating look at where AI is headed. From the explosive growth of open-source models to the rise of intelligent AI agents and the potential of voice interfaces, the future of AI is both exciting and challenging. As AI continues to evolve, it’s essential that we stay ahead of the curve, understanding both the opportunities and the risks involved.
Whether you’re a developer, a policymaker, or just an AI enthusiast, the time to pay attention is now. The organizations and governments that adapt quickly to these changes will shape the future of AI and set the pace for the next decade.
Call to Action:
Ready to dive deeper into the world of AI? Stay informed, keep exploring, and who knows—you might just be part of the next big leap in artificial intelligence. Stay tuned for more insights and updates!

